How to Prepare an Income Statement? The 8 basic steps (+FREE template!)
The Income Statement (in some countries called Profit and Loss) is a crucial part of financial reporting. It could help you understanding both your business as well as personal finances.
This article will help you with the following:
- How to calculate my profit?
- How does the income statement work?
- Is it possible to prepare an income statement on my own?
If you are asking these questions and want to find straightforward answers this article is for you!
At What a Figure! Accounting we will walk you through all the important points of this report.
What is an Income Statement?
The Income Statement is a report that summarizes a company’s income and expenses over a specific period of time. It is the most common financial statement because it is easy to understand and helps company owners to see how profitable a company is. The Profit and Loss Statement will often have the following sections:
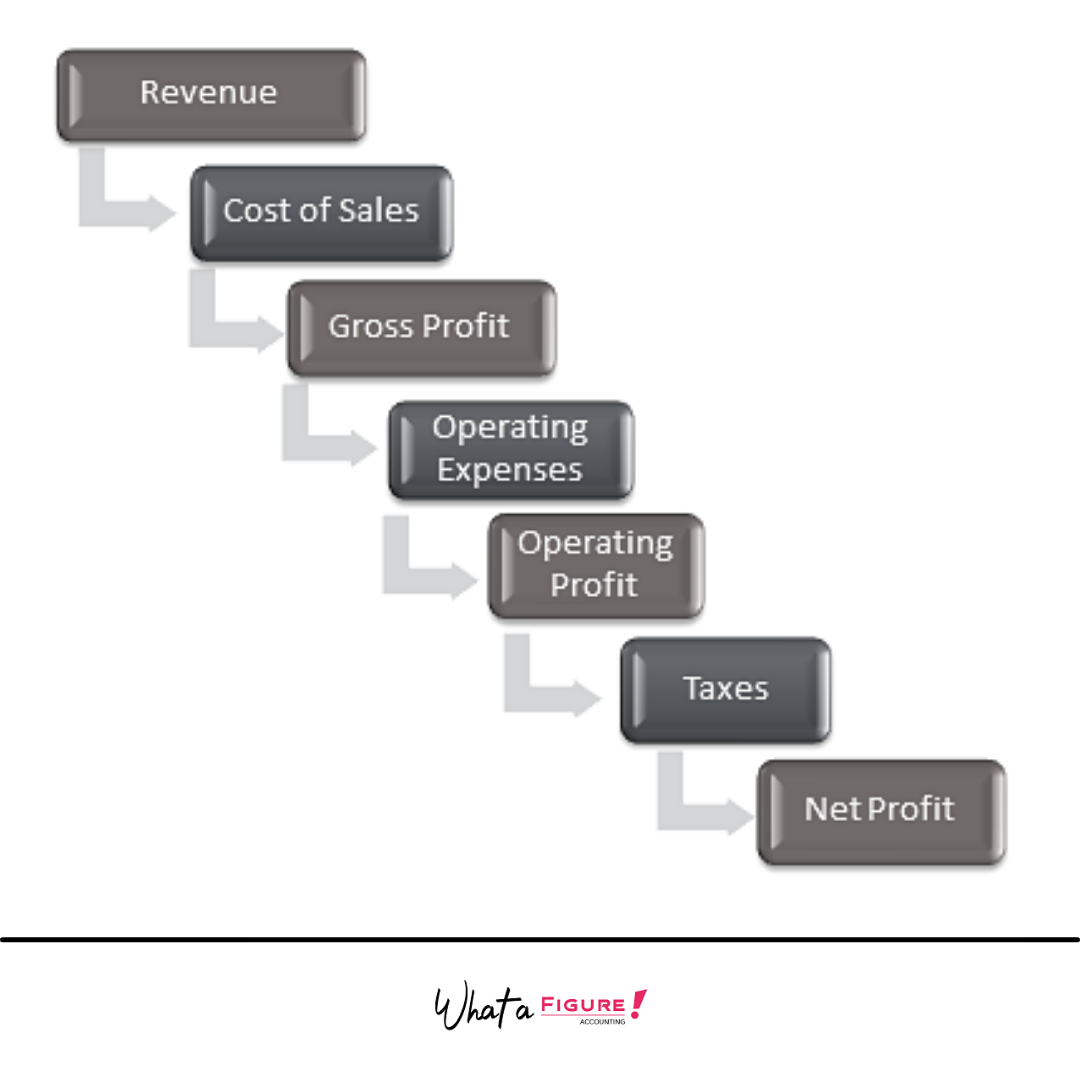
Imagine that the process of preparing the income statement is a journey from the top (total revenue) to the bottom (net profit) like in the picture above. Following these steps, you should deduct all related expenses (blue boxes) to exactly determine how much is left in your pocket (Net Profit).
The connection between each of these section in P&L could be shown as a simple equation:
Revenue (Sales/Turnover) – Costs of Goods Sales – Operating Expenses – Non-Operating Expenses (Income Tax) = Net Profit
We will review each variable of this formula below in this post to get an idea of how to prepare an income statement.
Furthermore, to make it easy to understand, we will compare the whole process with examples from our personal finances.
The main steps to prepare an income statement
Step 1. Pick a Reporting Period
To prepare an income statement you need to decide what period you want to create it for. It is up to you, but to give you some guidance, these are the most common ones companies use:
- Monthly: for short term trends
- Quarterly: for a bigger picture and seasonal trends.
- Yearly: for company growth trends and bird eye view.
Whichever you pick, we highly recommend you to compare them with 1 or 2 previous periods (same length) to get a picture of the trend. Without comparison, you don’t know if you are doing better or worse than before.
Example:
Here is an example of how you can choose time frames for the income statement in Xero (this is an accounting software we are in love with:)
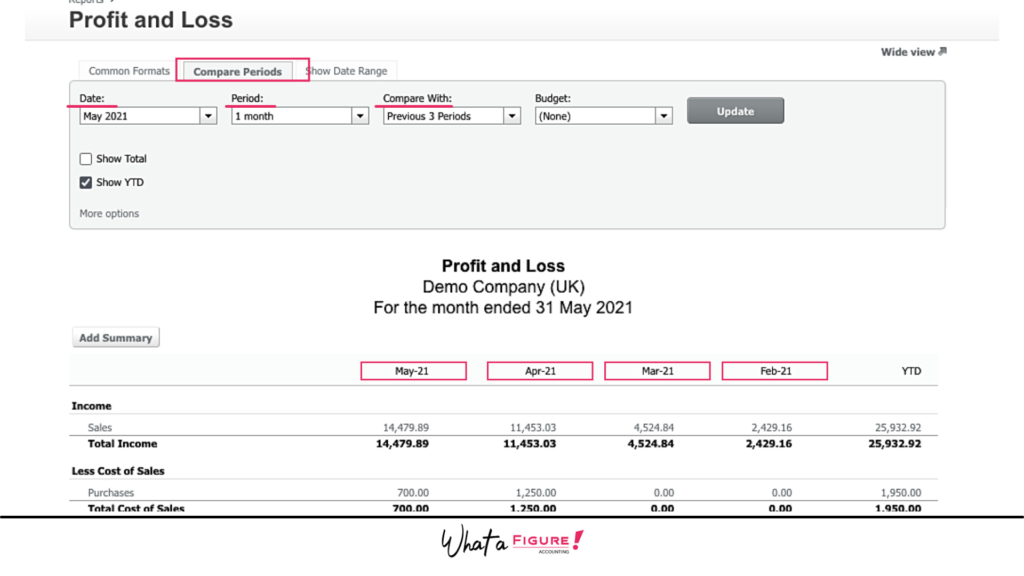
Step 2. Calculate Your Revenue
A company’s revenue is the total value of the goods and services sold over the selected period.
Revenues are also referred to as sales, income, or turnover.
When it comes to personal finances, this would be your gross salary for example – what you have earned before paying taxes and any other possible deductions.
It’s relatively straightforward to determine your turnover. If you’re keeping accurate records, it should be fairly easy to add together your total sales. Remember that turnover is measured over a specific period, for example, a tax year (the same period you selected in Step 1).
Step 3. Determine Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
In order to generate revenue you as an Amazon or e-commerce seller, you often incur some cost. The cost of materials and labor directly used to create the goods or services provided. This cost is the cost of goods sold.
Let’s look at it from a personal finance perspective again. To earn your salary (revenue) you need to get to the office every day. Therefore, transportation expenses will be your direct costs. If you are studying and paying for educational courses connected with your work these could also be referred to as direct expenses.
If you are a dropshipper your COGS includes money spent on purchasing goods which you later sold at a markup to your customers. So, e-commerce sellers’ direct costs usually include purchase cost per SKU including shipping.
You can find more information about the cost of sales here:
Step 4. Calculate the Gross Profit
Gross profit is the difference between total revenue and the cost of the goods sold.
What does it tell you?
- It shows whether revenue could cover costs associated with the production of goods/services.
- Additionally, it tells you what % of your costs are variable costs. Cost of goods sold (direct costs) are variable. Meaning you don’t incur them, unless you have revenue. Whereas overheads (which we will discuss shortly) are fixed costs (eg. rent). You will incur them irrelevant if you sold anything or not.
Amazon and e-commerce sellers often have a rather high COGS (approx 30% or revenue) and therefore lower gross profit margin (gross profit / revenue), than for example Software Companies do (whose COGS is usually around 5-10% of their revenue).
The lower your COGS is, the higher your gross profit is. It means higher gross profit margin. Businesses with higher gross profit ratio are usually easier and faster to scale.
If your sales can hardly cover the money you spent on sold items, you should change your pricing strategy or search for another supplier.
Step 5. Include Operating Expenses
Operating expenses (or also called overheads) include the costs associated with running your business, such as rent, advertising, insurance or the cost of operating your computers.
These are fixed expenses: irrelevant whether you generate any revenue or not, you will incur these expenses. This is why many early stage startups file losses in the first few years of their trading.
In personal finance, ‘operating expenses’ would be food, rent etc.
Operating expenses are the costs that a company incurs in order to operate its business on a day-to-day basis.
Step 6. Calculate Your Income Before Taxes
Business income before taxes refers to the profit before deducting the tax expense from it. This figure is also known as Operating Profit.
Step 7. Include Income Taxes
Probably, you heard a famous saying that there’s nothing more certain than death and taxes.
If you have an income you must pay taxes.
In accounting, income tax expense refers to the total amount of income tax that a company has to pay during for the financial year.
Fiscal responsibility is an important part of running a successful business as well as managing your personal wealth.
Step 8. Calculate Net Income
Lastly, we got to the bottom line of the income statement. Net income represents the amount of profit a company has earned after all expenses have been paid. A negative net income – often shown in brackets eg. (£10,347) means that the business lost money during the reporting period, while a positive net income indicates a profit. The net income figure is one of the most important measures of the financial health of a business. The net profit is the bottom line of the income statement. It can also be referred to as the net income, the bottom line, or the net earnings.Income Statement Example (FREE template!)

*YTD (last column) means ‘Year-to-date’ results, which is all the income and expenses since your current financial year started.
In some cases, it’s better to start with a simple spreadsheet (if you have very few transactions or even just want to practice and get a better understanding of how it works ). You can find a free template here. We have listed there the most common revenue and expense accounts for business, however, you can change it according to your needs.
Income Statement in Xero: general overview
Track all your sales and expenses manually can be very tedious and time consuming. Fortunately, nowadays you can generate all financial statements by using accounting software and rely on a professional bookkeeper. It’s extremely easy to run your e-commerce business’s finances with the help of Xero accounting software. Most of the e-commerce sellers love this software as Xero could be integrated with online stores (Shopify, BigCommerce, etc). Amazon account could also be easily connected with this accounting software. All your financial data like sales, refunds, fees, etc. will be seamlessly flowing into the system. Thankfully, there is no need to input all data to Xero manually (for busy e-commerce sellers, it’s almost impossible). Specialized third-party apps like A2X or Weava can make this work a breeze for you. You can automate the bookkeeping process and get accurate, up-to-date financial statements whenever you need them. Another beautiful feature of Xero is that you can customize the Profit and Loss layout depending on your needs. By default, the P&L layout will look like this: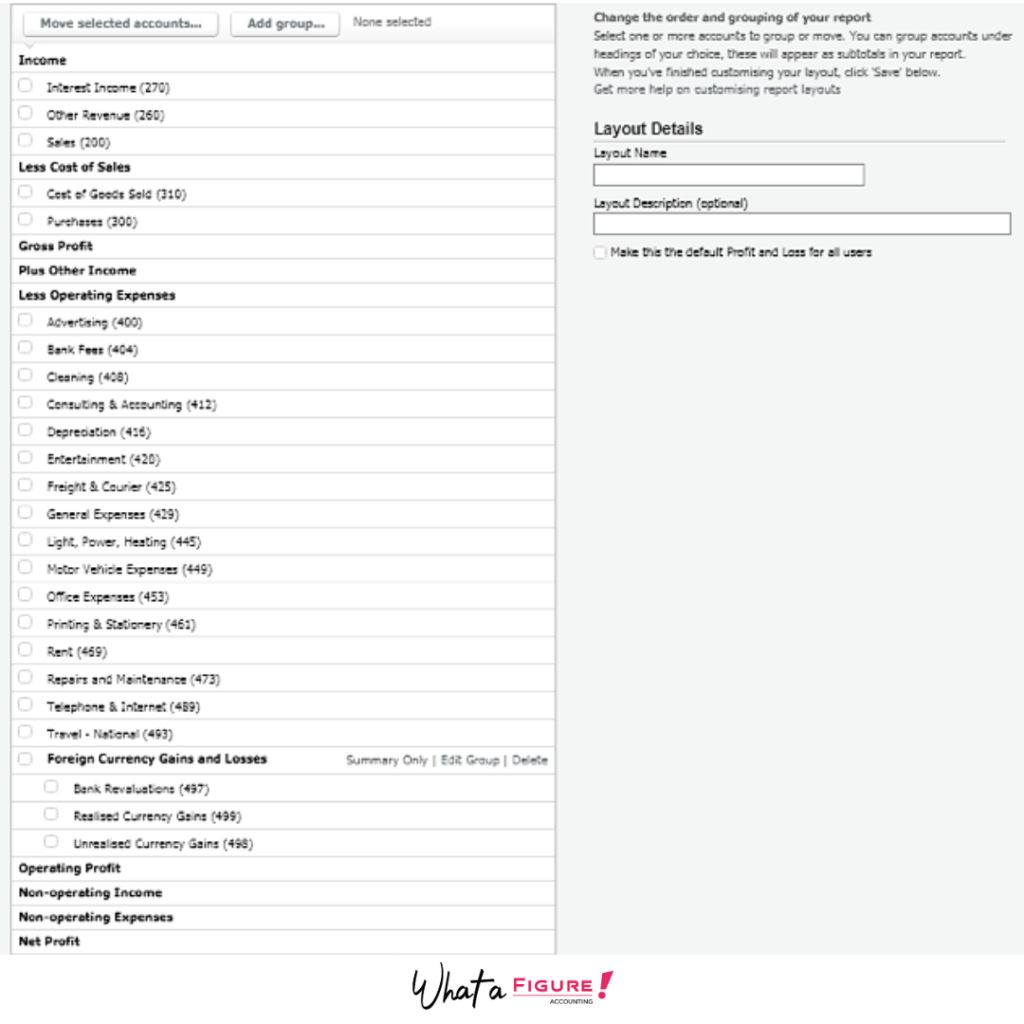
Xero allows you to group accounts in your Profit and Loss statement based on your preferences and the nature of your business.
Furthermore, you can customize your chart of accounts and make financial reporting more ‘visual’ and clear for you.
If you are selling on Amazon, you can create separate accounts for shipping and Amazon fees. Furthermore, you can divide your sales revenue by creating a separate account for each channel (Amazon UK, Amazon Japan, Amazon Australia etc). It will give you a great overview on your Profit & Loss Statement.
Another option for creating informative financial statements is setting up tracking categories for each sales channel you use. You can assign revenue and related costs for each category. As a result, Xero could compare the profitability of each channel and give you a really deep insight into the financial position of your business.
How could you benefit from an Income Statement?
The income statement is the best tool for analyzing your earnings and costs. By comparing a few periods in a row you can get an idea of how your revenue and expenses changed over time. You can determine whether you can (or should) cut costs that could lead to increasing your profit. Furthermore, you can see how your profit is growing and what the main contributing income sources are. If you prepare an income statement on a regular basis you can also notice negative trends and eliminate them as early as possible. Every business owner should develop a habit to review this financial statement. The ability to track your business’s performance is a core benefit you should stay on top of. Furthermore, it is a valuable source of financial information for investors. The income statement will be one of the first thing they will be looking at.What are the limitations of the Income Statement?
The tricky and often misleading part of the income statement is the fact that high profit doesn’t always mean you have cash in hand to meet your financial obligations. This is often the case when the business does accounting on an accrual basis. In other words, accrual accounting means that the business records the revenue to the income statement even though the customers haven’t paid yet. If you want to assess how much cash there will be available in the near future you should refer to the cashflow forecast instead. If you want to analyze the solvency and liquidity of the company you can’t do it without the balance sheet. Therefore, it is a good idea to analyze the three main financial reports together. Another thing to keep in mind is that the Income Stement could include estimates (assumptions) instead of actual figures. Sometimes bookkeepers need to account for costs before receiving a bill from the supplier or estimate revenue for services that are in progress and haven’t been invoiced yet. Often, it is impossible to post accurate accruals (estimates) without adjusting them in the next periods. So, the income statement doesn’t always reflect accurate costs and earnings. The company may report a slightly high sales.. Hence the actual revenue may be lower. Amazon and e-commerce sellers are less prone to this.We hope that the above article helped you understand how the income statement is prepared and what valuable information it could bring to your e-commerce business. If you have any questions please let us know in the comments below!

